First Warnings of Endocrine Disruptors
Air Date: Week of April 17, 2015
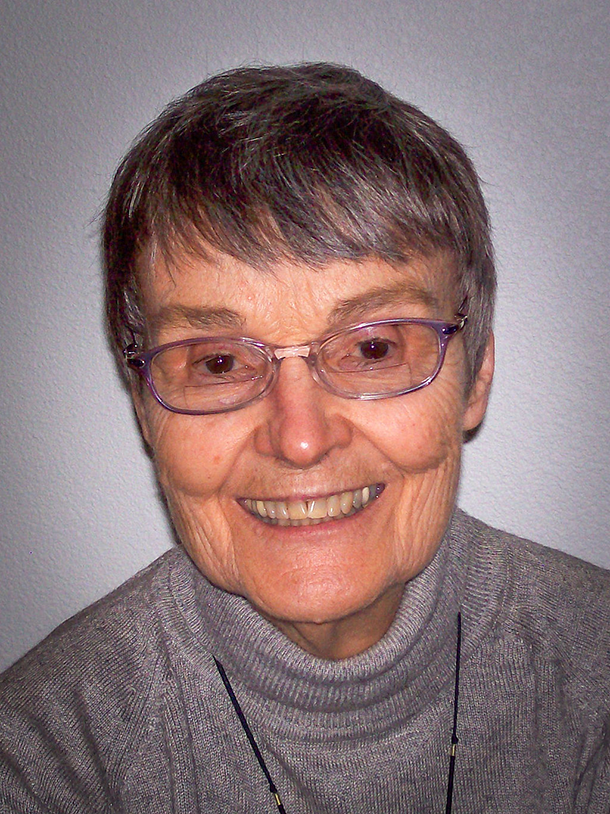

Theo Colborn, one of the first scientists to warn the public about the dangers of endocrine disrupting chemicals. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons; CC BY SA-4.0)
Common synthetic chemicals that surround us and are in countless products can get into the human body and affect the immune system, intelligence and the reproductive system. In 1994, host Steve Curwood followed the investigative trail of these endocrine disruptors, and spoke with Theodora (Theo) Colborn, one of the first scientists to sound the alarm about the effects these chemicals can have on organisms and the environment.
Transcript
CURWOOD: It’s Living on Earth. I’m Steve Curwood. Many scientists believe global warming is the greatest threat facing the planet, but it’s hardly the only threat in our environment. Other dangers include the many powerful chemicals now found everywhere in our earth and water, and in this season of the 45th Earth Day we’re taking the opportunity to remember one of the most innovative environmental scientists of recent times, Theodora Colborn. It was Theo who first correlated the data suggesting that tiny doses of many common chemicals such as plasticizers and pesticides could mimic hormones in humans and wildlife, with effects that might include depressed sperm counts, and a heightened incidence of the painful condition, endometriosis. In 1994, Theo Colborn, then a senior scientist at the World Wildlife Fund, explained her ideas on Living on Earth.
COLBORN: I think we have flooded the environment with a large number of chemicals that look like or interfere with hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, and inhibiting substances.
CURWOOD: Dr. Colborn calls these chemicals endocrine disrupters. The endocrine system is the delicate network of glands which produce hormones: the powerful chemical messengers which regulate our most vital biological processes, including sexual development, immune response, and the way we react to stress. Natural hormones are intensely powerful, but quickly eliminated by our bodies. Synthetic chemicals which act like hormones, on the other hand, are much weaker, but our bodies don't know how to get rid of them, and they build up, mostly in our fat. Dr. Colborn worries that the most important impact of these substances may not be on the people directly exposed to them, but on the next generation: on their offspring. In pregnant women, Dr. Colborn says, hormone-imitating chemicals can leech out of fat cells, cross through the placenta, and wreak havoc on the fetus at the most vulnerable stages of development.
COLBORN: They look like hormones, and they are capable of getting into the body and interfering with the normal hormonal activity, and the messages, the normal messages, that control normal growth.
CURWOOD: Many of the chemicals that Dr. Colborn suspects are endocrine disrupters are tested for their ability to cause cancer and birth defects, but they are not tested for what she says may be their less obvious, but no less devastating impact.
COLBORN: We had been focusing on cancer and mutations. We've been sidetracked by that, and we've missed this other, really more insidious effect. If the immune system is affected maybe they're not well all the time. If their nervous system is affected, maybe they're not as smart as they should be. Maybe they have problems with behavior. Maybe we're affecting their fertility, so that population may not be able to reproduce eventually.
CURWOOD: And these chemicals are all around us now. All the time.
COLBORN: That's right. That's right. Steve, you're sitting there right now with at least 500 measurable chemicals in your body that were not there before 1940. And I think what's happening is that you can't predict what these chemicals are going to do.
CURWOOD: Some of the substances that Dr. Colborn suspects are endocrine disrupters are heavy metals. Cadmium, lead, and mercury. But most come from a class of chemicals called organochlorines. They are used in thousands of products from pesticides and plastics to pharmaceuticals. DDT and PCBs are organochlorines that were banned because scientists believe they cause cancer. But even that link is uncertain. In fact, so little is known about so many of these chemicals that critics charge Dr. Colborn's theory is just that: a theory and nothing more. But after years of analyzing research from around the world, Dr. Colborn is convinced by what she's seen.
COLBORN: There was a consistency to what I was finding. It's called what I call the weight of evidence approach.
CURWOOD: That’s Theo Colborn, speaking on Living on Earth back in 1994.
Links
Hormone Disruptors Linked To Genital Changes and Sexual Preference
BPA-Free Does Not Always Mean Safe
Living on Earth wants to hear from you!
Living on Earth
62 Calef Highway, Suite 212
Lee, NH 03861
Telephone: 617-287-4121
E-mail: comments@loe.org
Newsletter [Click here]
Donate to Living on Earth!
Living on Earth is an independent media program and relies entirely on contributions from listeners and institutions supporting public service. Please donate now to preserve an independent environmental voice.
NewsletterLiving on Earth offers a weekly delivery of the show's rundown to your mailbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
 Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
 The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
 Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
 Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth
Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth